View Answer The boiling point of methanol is 65 degrees Celsius and the. This synthesis application is described in the following equations.

Draw The Mechanism And Show The Products With Correct Stereochemistry For The Following Sn2 Reactio Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry Lessons
Because the acetylide anion is a powerful nucleophile it may displace halide ions from 1º-alkyl halides to give a more highly substituted alkyne as a product S N 2 reaction.

. The following web-sites provide nice collections of problems and answers. So no S N 1 or S N 2 in nucleophilic aromatic substitutions. For an E1 reaction.
MIT Open CourseWare Reaction quizzes and summaries from Towson University Electronic flashcards from Ohio State University. The fact that the substitution occurs on the α-carbon led Lapworth to propose that the more reactive form was an enol tautomer of acetone. The bromine atom leaves with its bonding electrons as a bromide ion.
Instead the reaction occurs either by addition-elimination or elimination-addition mechanism. Unimolecular elimination E1 is a reaction in which the removal of an HX substituent results in the formation of a double bond. Nucleophilic substitution with cyanide ions.
Synthetic Uses for α-Halogenated Carbonyls. Consequently the benzylic substituent will become and Iodide product and the propyl substituent. For the reaction proposed above the reactant contains a benzylic substituent so the reaction will most likely be S N 1.
The cyanide ion attacks at the partially positive carbon of the dipole making a high energy transition state. The nucleophilic substitution reactions of ammonia and amines with halogenoalkanes to form primary secondary. Mechanisms of nucleophilic substitution.
The product of α-bromination can be converted to an α βunsaturated carbonyl by reaction with pyridine and heat by elimination of H and Br. These are the reactions of arene diazonium salts which are sort of unique and represent a good set of strategies in the chemistry of aromatic compounds. The addition-elimination mechanism is more common and starts with.
Apply IUPAC rules for nomenclature to draw the structure of an organic compound from the IUPAC name limited to chains and rings with up to six carbon atoms each. The tertiary alkyl substutent will form an alkene and the other alkyl substiutent will become an alcohol. It is similar to a unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction SN1 in particular because the rate determining step involves heterolysis losing the leaving group to form a carbocation intermediate.
The products of this acid-base reaction are ammonia and a sodium acetylide salt. Draw the substitution product that would result if the bromine bonded to the para carbon instead of the benzylic carbon. The final product is a nitrile.
Most organic chemistry textbooks contain a broad assortment of suitable problems and paperback collections of practice problems are also available. Distillation of a product from a reaction.
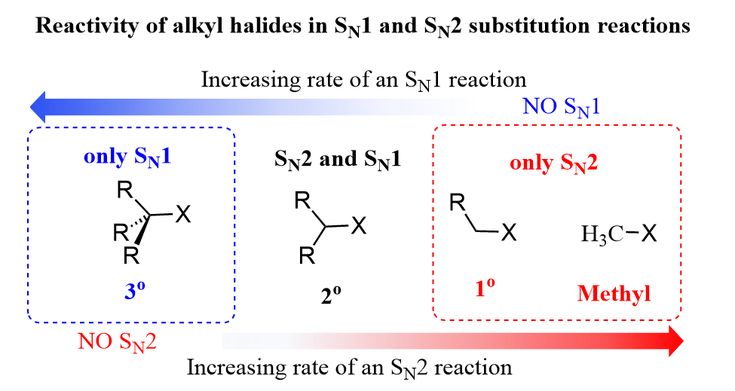
Sn1 Sn2 Reactivity Of Alkyl Halides Organic Chemistry Sn1 Sn2 Organic Chemistry Study

Carbocation Rearrangements In Sn1 Reactions Practice Problems Organic Chemistry Chemistry Lessons Chemistry

Introduction To Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Practice Problems Reactions Organic Chemistry Chemistry

Organic Chemistry Practice Problems Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Reactions Organic Chemistry Study

Determine Based On The Identity Of The Substrate Nucleophile And Solvent The Mechanism Of Nucleophilic Substitution Of Chemistry Organic Chemistry Sn1 Sn2

The Energy Diagram Of The Sn2 Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction Organic Chemistry Books Reactions Tricky Questions

Organic Chemistry Practice Problems Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Reactions Organic Chemistry Study

Draw The Mechanism And Show The Products For The Following Sn2 Reactions Paint Program Online Painting Painting Teacher
0 comments
Post a Comment